Rogue second that brought down the Internet
It might not have been the Millennium Bug, but an unexpected second added to the world’s clocks wreaked havoc on the software of many of the world’s leading websites, taking them out for hours.
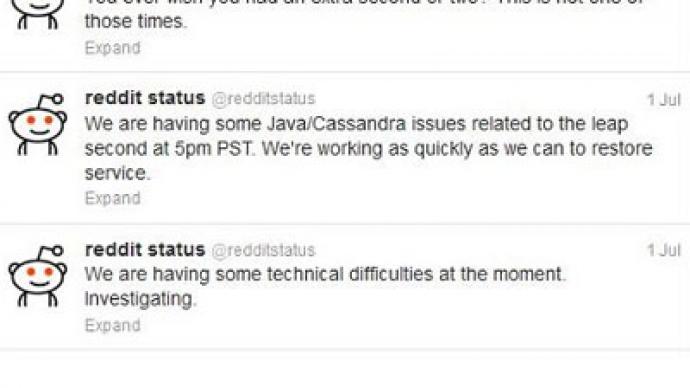
Social news websites Reddit and Gawker, professional network LinkedIn, and geolocation application Foursquare are just some of the popular sites that were unavailable or worked incorrectly throughout Sunday.The cause: a leap second.Like Greenwich Mean Time before it, UTC is the “gold standard” of time, measuring it with precise atomic clocks and is used by most computer programs.To account for the minuscule changes in the Earth’s speed of rotation UTC sometimes adds a second to make sure that the relation between the time of day of the position of the Earth and the Sun always remain the same.UTC added a leap second between Saturday and Sunday for the first time since 2007.And some websites – many of which did not exist five years ago – were confused by the extra second, with their commands going haywire, or shutting down altogether from receiving an unfamiliar instruction to add a second coming from the UTC servers.“Ever wish you had a second or two? This is not one of those times,” posted the official Reddit Twitter account, as its engineers scrambled to reset their software.Being aware of the problem beforehand, Google created a special program that made its seconds slightly longer all the way through Saturday, so that there was no need for any synchronization at midnight.The shutdown was reminiscent of the mooted effects of the Millennium Bug, when there wasa switch over of the clocks from ’99 to ’00 on two-digit computer clocks on 31 December 1999.More than $300 billion was spent on updating software to comply with the date change, but even in those computers that were not proofed against it, major failures were rare.As a result, date switch fears have been viewed as largely overblown.But the leap second crash shows that unusual time changes can still trip up software used by millions worldwide.